pH Meter
Digital pH Meter for Water/Chemistry/Medicine, ORP Test
Portable pH Meter, ORP Test / Temperature Compensation
Industrial pH Meter for Wastewater/Laboratory/Flue Gas Desulfurization
Benchtop pH Meter, 6 in 1 pH/ORP/Temp/TDS/EC/CF
4 in1 pH Pen, pH/EC/TDS/Temp
pH Meter for Fish Tank with Temperature Compensation
pH Multimeter, pH/Salt/Temp/TDS/EC
3 in 1 Pen Type pH Meter, pH/TDS/Temp
Handheld pH Meter for Industrial Water Testing
Soil pH Monitor, Soil Moisture/Temperature/pH
Pool pH Tester for Cl & pH
pH Tester for Aquarium, Online Wall-mounted
pH Meter Electrode for Strong Acid or Alkali
pH Meter Electrode for Chemical
Flat pH Meter Electrode
pH Meter Electrode for Food
Combination pH Electrode for Water
High Temperature pH Electrode for Pharmacy / Brewery / Desulphurization
High Precision Glass pH Meter Electrode
What is pH Meters
A pH meter is a scientific instrument used to measure the hydrogen ion concentration in solutions, determining the acidity or alkalinity, commonly expressed as a pH value. It works by using a specialized glass electrode sensitive to hydrogen ions, along with a reference electrode, to measure the voltage difference between them in a liquid sample. This voltage is then converted into a pH value, typically displayed digitally. pH meters are crucial tools in various fields such as chemistry, biology, environmental science, agriculture, and industry. They help in processes like water quality testing, chemical production, soil analysis, and food and beverage manufacturing, where maintaining the right pH balance is critical for efficiency, safety, and quality control. With different types like portable, laboratory, and online meters, they cater to diverse application needs, ensuring precision and reliability in pH measurement.
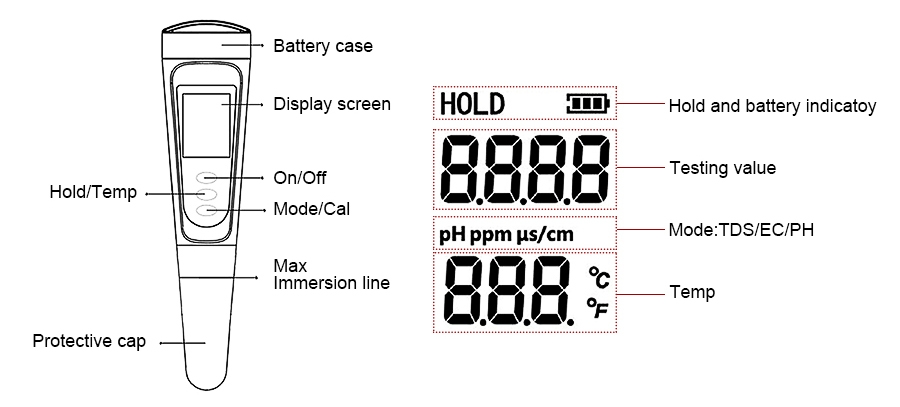
Components and Working Principles of pH Meters
The core component of a pH meter is its electrode system, which typically includes a glass electrode and a reference electrode. The glass electrode is sensitive to hydrogen ions, reacting with them to generate a potential difference that correlates to the solution’s pH. However, glass electrodes are fragile and require careful handling to prevent damage. The reference electrode provides a stable, known potential, which remains unaffected by the hydrogen ion concentration in the solution. Together, these electrodes measure the potential difference, allowing for accurate pH readings. Advanced pH meters may feature combination electrodes, which merge the glass and reference electrodes into a single unit, simplifying operation and reducing maintenance.
The display unit of a pH meter converts the electrical signals generated by the electrodes into a readable pH value. Traditional analog meters used dial displays with pointers, which were prone to reading errors and subjective interpretation. Modern pH meters, however, feature digital displays with LCD or LED screens that provide precise numeric readouts, often to two decimal places or more. Digital displays also commonly offer additional features such as data logging, temperature compensation, calibration reminders, and automatic shutoff. Temperature compensation is crucial in pH measurement, as the pH of a solution can fluctuate with temperature changes. Many pH meters are equipped with automatic temperature compensation (ATC) to adjust readings for these variations, ensuring accurate measurements regardless of the surrounding conditions. Basic pH meters may require manual input of temperature values for compensation.
Power supply options for pH meters vary depending on their type. Portable and pen-style pH meters typically use batteries, such as 9V or button cells, allowing for easy mobility. Laboratory and online pH meters, designed for continuous and long-term use, are usually powered by external sources. Modern portable and lab models may feature rechargeable batteries with indicators to alert users when recharging is needed. Regardless of the power source, the performance of a pH meter depends on the quality of its components and the coordination between them. Proper calibration, electrode maintenance, and temperature compensation are essential for ensuring reliable and accurate pH readings in any application.
Types of pH Meters
pH meters are essential instruments used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of solutions. There are several types of pH meters, each designed for different applications. Portable pH meters are compact and lightweight, making them ideal for fieldwork or mobile testing environments, such as agricultural soil and water quality testing, environmental monitoring, and pond water management. Though portable pH meters offer quick and simple operation, they may not match the accuracy of more advanced models, making them suitable for rough, on-the-go measurements. Laboratory pH meters, on the other hand, are highly precise instruments used in controlled environments where accuracy is paramount. These meters feature high-precision electrodes, advanced temperature compensation systems, and multi-point calibration, which makes them ideal for chemical research, food and beverage quality control, and biomedical experiments. They are known for their extensive data storage and export capabilities, although their larger size and higher cost often limit them to stationary use in labs.
For industrial applications, online pH meters are frequently employed to monitor processes in real-time. These meters are installed in pipelines or tanks, continuously measuring pH levels in environments such as chemical plants, wastewater treatment facilities, and food production lines. They typically include automation and alarm systems that trigger when pH values exceed safe limits, ensuring optimal conditions are maintained throughout production. While these systems offer high levels of automation and accuracy, they require more complex installation and maintenance, and their initial investment can be high. Pen-style pH meters are the most compact option, shaped like a pen for easy portability. They are popular for simple tasks such as household water quality tests, aquarium maintenance, and basic soil testing. However, pen-style meters offer lower accuracy and a shorter lifespan, making them more suitable for everyday, non-critical applications.
Why pH Meters is Important
pH meters are vital tools in various industries and scientific fields because they provide accurate measurements of a solution's acidity or alkalinity, which is critical for maintaining optimal conditions in numerous processes. In water treatment, pH meters help ensure safe drinking water and proper wastewater management by monitoring and controlling pH levels to avoid harmful conditions. In agriculture, soil pH plays a key role in nutrient availability for crops, and using a pH meter allows farmers to adjust soil conditions for better plant growth. In the food and beverage industry, maintaining the correct pH is essential for product quality, taste, and preservation, especially in products like dairy, wine, and beer. Moreover, in laboratories and medical fields, pH meters are used to conduct precise chemical experiments and monitor bodily fluids, aiding in diagnosis and treatment. The ability to maintain and monitor pH accurately through pH meters ensures safety, product quality, and efficiency in numerous critical applications.




















